Source of this article and featured image is TechCrunch. Description and key fact are generated by Codevision AI system.
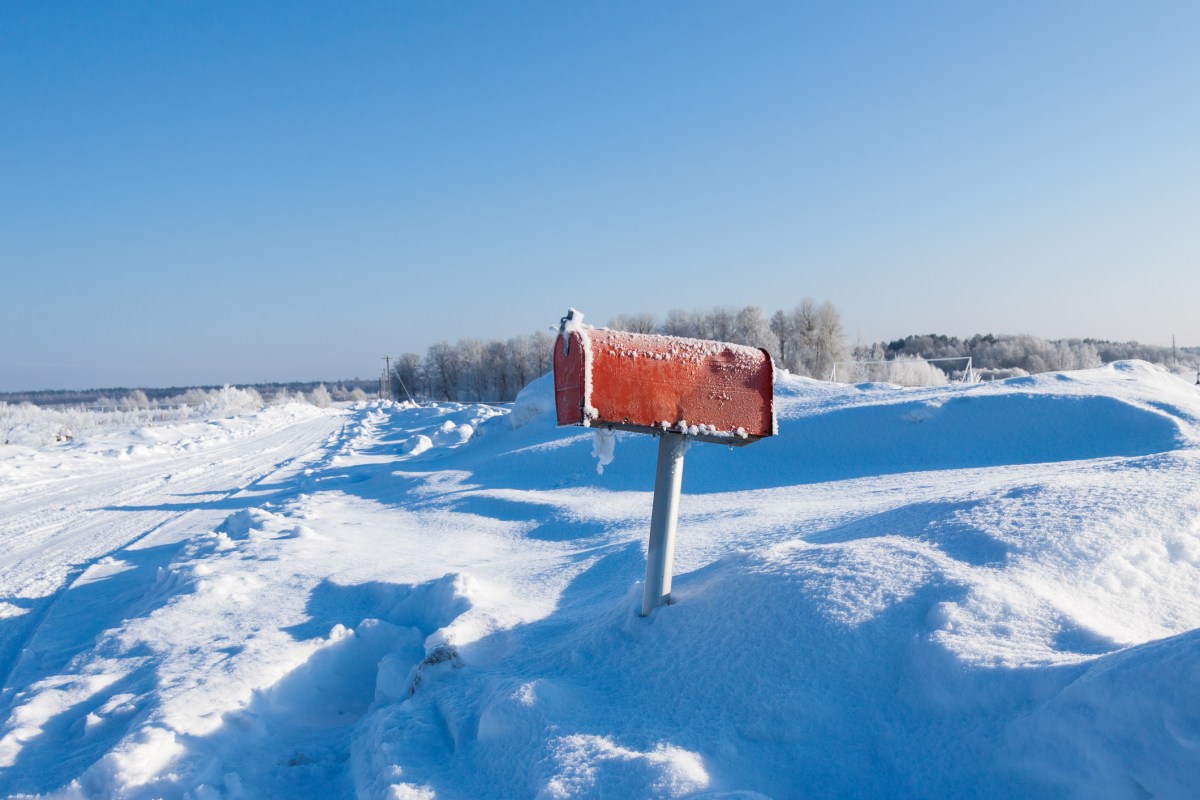
Data centers are increasing electricity demand across North America, raising concerns about grid stability during winter storms. A 2.5% rise in winter energy needs, reaching 20 gigawatts, has been flagged by NERC as a potential risk. Regions like Texas face heightened vulnerability due to rapid data center expansion and past infrastructure weaknesses. While battery storage has improved grid resilience, prolonged cold snaps could still strain power supplies. NERC warns that severe storms may force grid operators to implement blackouts or demand cuts if energy shortages persist.
Key facts
- North America’s winter electricity demand is projected to rise 2.5% compared to last year, reaching 20 gigawatts.
- Data centers are a major driver of this growth, particularly in the U.S. mid-Atlantic, West, and Southeast regions.
- Texas’s data center expansion increases the risk of supply shortfalls during extreme weather events.
- The 2021 Texas blackout was caused by frozen natural gas plants and surging residential/commercial energy demand.
- Batteries now help stabilize Texas’s grid, but they may struggle to meet continuous data center energy needs during prolonged cold snaps.
TAGS:
#blackout risks #data centers #electricity demand #energy supply #grid stability #NERC report #power outages #reliability assessments #Texas blackout #winter storms